Uti Tests And Diagnosis
If you suspect that you have a urinary tract infection, go to the doctor. You’ll give a urine sample to test for UTI-causing bacteria.
If you get frequent UTIs and your doctor suspects a problem in your urinary tract, they might take a closer look with an ultrasound, a CT scan, or an MRI scan. They might also use a long, flexible tube called a cystoscope to look inside your urethra and bladder.
There Are Several Different Types Of Utis
Healthline does say that bladder infections are the most common type of urinary tract infection so if you are experiencing burning pain when you urinate and only a few drops come out every time you go, then yes, you very likely have a bladder infection. You may also feel a certain amount of pain in your pelvic or pubic area with this type of infection. If you have urethritis, which is an infection in your urethra , you may feel some itching when you pee.
With a kidney infection, the most serious type of UTI, you may experience the same symptoms you would with a bladder infection. There could also be other signs of trouble like blood in your urine, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, severe back pain, nausea, vomiting, chills, and/or fever. Once these symptoms kick in, get yourself to a doctor, stat! You’ve only got two kidneys, and if anything happens to them, you could be at risk of serious complications. In fact, kidney infections left untreated can even prove to be fatal, so they are nothing to mess around with .
Whether you think you have a bladder infection or a different type of UTI, you should speak with your doctor.
Prevention Of Urinary Tract Infections
In order to prevent the development of UTIs, it is important to drink plenty of water, urinate when you feel the urge, rather than holding urine for extended periods, and urinate after intercourse. Certain substances, such as cranberry pills, lactobacillus, and methenamine may be prescribed to those who are frequently afflicted by UTIs.
Also Check: Does Nitrofurantoin Treat Kidney Infection
Vaccines Targeting Bacterial Toxins And Proteases
The UPEC pore-forming toxin HlyA has also received attention as a potential vaccine target and was evaluated in a mouse model of pyelonephritis to assess protection against renal damage114,115. Vaccination with HlyA reduced the incidence of renal scaring compared with controls however, it did not protect against UPEC colonization of the kidneys115. In addition, in a mouse model of UTI, vaccination with the P. mirabilis haemolysin, HpmA, did not provide protection against bacterial colonization116. However, vaccination with Pta, an alkaline protease with toxic effects towards epithelial cells, displayed promising results in a mouse model of UTI, protecting against upper UTI, although bacterial burdens in the bladder remained unaffected116. Thus, although haemolysins and proteases might provide effective vaccine targets for preventing upper UTIs, additional studies are needed to determine the effectiveness of these enzymes as targets for vaccines.
Recommended Reading: How Do Doctors Treat A Kidney Infection
Small Molecules Targeting Bacterial Adhesion
Our detailed understanding of pilus assembly and pilusreceptor binding has opened the door to the development of two classes of small, rationally designed synthetic compounds to inhibit pili: mannosides, which inhibit pilus function and pilicides, which inhibit pilus assembly. Targeting CUP pilus function or assembly has therapeutic potential, as it should block UPEC colonization, invasion and biofilm formation, thus preventing disease,,,.
Mannosides, which are FimH receptor analogues, have been developed to bind FimH with high affinity and block FimH binding to mannosylated receptors,,. Mannosides are potent FimH antagonists that offer a promising therapeutic opportunity for the treatment and prevention of UTIs by interrupting key hostpathogen interactions. Studies in mouse models have demonstrated the potential of mannosides as novel therapeutic strategies against UTIs: mannosides are orally bioavailable they are potent and fast-acting therapeutics in treating and preventing UTIs they function by preventing bladder colonization and invasion they are effective against multidrug-resistant UPEC they potentiate antibiotic efficacy and they are effective against established UTIs and CAUTIs,,,.
Read Also: Natural Ways To Get Rid Of A Tooth Infection
How To Tell If You Have A Bladder Infection Vs Uti
Is there any feeling more horrible than when you start to feel something going wrong “down there?” You’ve got to pee every two minutes, to the point where you dare not stray more than a few steps from a bathroom but the only thing worse than the constant need to go is the fact that when you do, it hurts! It’s an all too familiar feeling for many women, but even men get bladder infections, too .
Your first thought, once you feel an infection coming on, is how to stop the pain and discomfort. Do you drink a quart of water, knock back a few glasses of cranberry juice, or see what over-the-counter treatments your local drugstore has to offer? Alternatively, should you make an appointment with your doctor? If you choose this last option, though, you may be wondering, “just what, exactly, should I tell them is wrong? Do I have a urinary tract infection , or could it be a bladder infection instead?”
Well, as Healthline points out, it’s either one thing, or it’s both. Bladder infections are actually a type of urinary tract infection, but they aren’t the only kind.
Is A Bladder Infection The Same As A Urinary Tract Infection
Often, the terms UTI and bladder infection are used interchangeably. But there is a distinction to be made between the two.
Bladder infections are a type of UTI, but not all urinary tract infections are bladder infections. A UTI is defined as an infection in one or more places in the urinary tractthe ureters, kidneys, urethra, and/or bladder. A bladder infection is a UTI thats only located in the bladder.
Read Also: Antibiotic Drops For Eye Infection
Uti Causes And Risk Factors
The most common cause of a UTI in the urethra is a sexually transmitted disease. Chlamydia and gonorrhea are two STDs that can cause a UTI. STDs are also the most common cause of UTIs in younger men.
Prostate problems can also cause UTIs. An enlarged prostate is common in older men and can block the flow of urine. This can increase the odds that bacteria will build up and cause a UTI.
Prostatitis, which is an infection of the prostate, shares many of the same symptoms as UTIs.
Diabetes and other medical issues that affect your immune system can also make you more likely to get a UTI.
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Utis
UTIs can cause such signs as:
- pain, burning, or a stinging sensation when peeing
- an increased urge or more frequent need to pee
- waking up at night a lot to go to the bathroom
- belly pain in the area of the bladder
- foul-smelling pee that may look cloudy or contain blood
If you have any symptoms of a UTI, you’ll need to go to a doctor right away. The sooner you begin treatment, the less uncomfortable you’ll be. Call your doctor’s office or clinic. If you can’t reach your doctor, you can visit an urgent care center or hospital emergency room. The most important thing is to take action as soon as possible.
Read Also: Rx Ear Drops For Ear Infection
How Is A Uti Diagnosed
To find out whether you have a UTI, your doctor or nurse will test a clean sample of your urine. This means you will first wipe your genital area with a special wipe. Then you will collect your urine in midstream in a cup. Your doctor or nurse may then test your urine for bacteria to see whether you have a UTI, which can take a few days.
If you have had a UTI before, your doctor may order more tests to rule out other problems. These tests may include:
- A cystogram. This is a special type of x-ray of your urinary tract. These x-rays can show any problems, including swelling or kidney stones.
- A cystoscopic exam. The cystoscope is a small tube the doctor puts into the urethra to see inside of the urethra and bladder for any problems.
Are There Any Over
Over-the-counter antibiotics for a UTI are not available. You should see your doctor to have your symptoms evaluated.
Your provider may recommend an OTC product called Uristat to numb your bladder and urethra to ease the burning pain during urination. Uristat can be bought without a prescription at the pharmacy. A similar phenazopyridine product called Pyridium is also available.
Take phenazopyridine for only 48 hours, and be aware it may cause your urine to turn a brown, orange or red color which may stain fabrics or contact lenses. It may be best to not wear contact lenses while being treated with phenazopyridine.
Phenazopyridine is not an antibiotic and will not cure a UTI.
See also: Ratings of Urinary Anti-Infectives
Don’t Miss: Can You Stop A Urinary Tract Infection
Types Of Urinary Tract Infection In Dogs
As occurs with humans, a urinary infection in dogs receives different names depending on the area in which it is located. The major urinary tract infections fall under one of the following types:
- Urethritis: infection of the urethra.
- Cystitis: bladder infection.
- Nephritis or pyelonephritis: both kidney infections.
How Do You Get Urinary Tract Infections
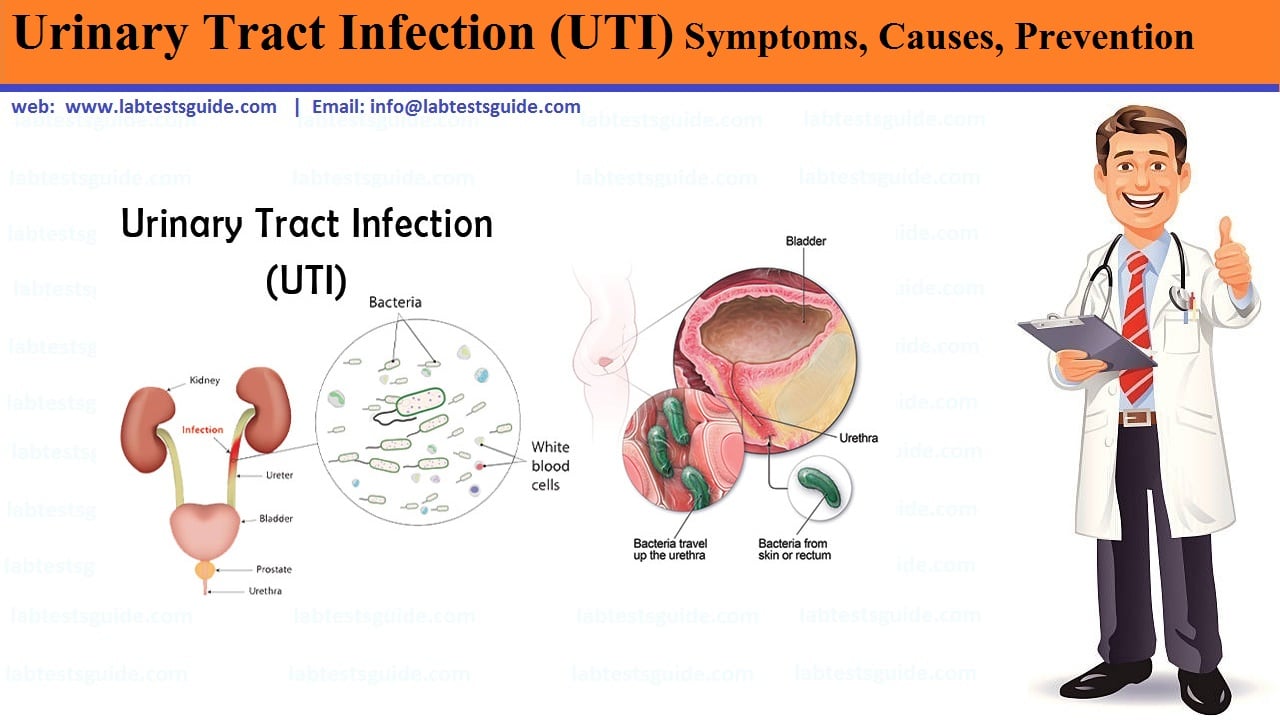
The design of the human body makes it so it isnt hard to get a bacterial UTI, because the infection comes from outside, through the urethra. Bacteria in the genital area can enter the urethra and the urinary tract, either because wiping after going to the bathroom, sexual activity, or unsanitary conditions. Once the bacteria have entered the urethra, the body tries fight them off, but sometimes the bacteria multiply and cause an infection.
In the case of a fungal infection, usually the fungus gets to the urinary tract through the blood stream. Those who develop this type of infection are usually ill with a disease that has compromised their immune system, such as AIDS.
Also Check: Over The Counter Meds Sinus Infection
Nux Vomica: For Frequent Urging To Pass Urine
Symptoms:
Nux vomica is a great healing agent for infection occurring in the urinary bladder.
There are pains in the lower abdomen. There is urgency and increased frequency for urination.
The quantity of urine is minimal. There is incomplete voiding of urine. While passing urine, there is an itching sensation. It is also helpful in UTIs occurring in people having alcoholic addictions.
Potency and Dosage:
You can use Nux vomica in 1M potency once daily at bedtime till improvement occurs.
You may also use Nux Vomica in 200ch potency twice daily till improvement occurs. In children, use Nux Vomica in 30ch potency twice daily till improvement occurs.
Other Rare Emerging Uti Bugs
- Aerococcus: a gram-positive cluster-forming bug that can cause life-threatening bladder, kidney, and blood infection if not addressed promptly.
- Corynebacterium urealyticum: a gram-positive bacterium that causes long-standing inflammation of the bladder and kidneys along with the formation of giant kidney stones.
- Actinobaculum schaalii: Possibly a gram-positive bug, resistant to first-line antibiotics used for treating UTI.
- Gardnerella vaginalis: Found in women with BV, can infect the bladder and kidneys.
You May Like: Tooth Infection And Chest Pain
Common Side Effects With Antibiotic Use
Each antibiotic is responsible for its own unique list of side effects, and the list is usually extensive. Be sure to discuss your individual antibiotic side effects with your healthcare provider. However, there are side effects that are common to most antibiotics, regardless of class or drug:
Related: Common Side Effects from Antibiotics, Allergies and Reactions
When To Seek Medical Advice
You are at greater risk of developing complications from a UTI and should seek medical advice promptly if you:
- have existing kidney disease, diabetes, or another chronic condition
- are over the age of 65
- or have one or more of the following symptoms high temperature , shivering, nausea and/or vomiting, diarrhoea or worsening pain in your abdomen, pelvis or back.
You May Like: Can You Get Rid Of A Tooth Infection At Home
Don’t Miss: Quick Home Remedies For Sinus Infection
What If I Have Frequent Recurring Utis
Within a year of havig a UTI infection, roughy one-quarter to one-half of women will have another UTI. For these women antibiotic prophylaxis may be recommended by her health care provider. With a recurrent course of UTIs, a urine culture or imaging tests may be required for further analysis.
For recurrent UTIs, there are several antibiotic options for prevention:
- A shorter course of antibiotics at the first sign of UTI symptoms a prescription may be given to you to keep at home.
- A longer course of low-dose antibiotic therapy.
- Take a single dose of an antibiotic after sexual intercourse.
The choice of antibiotic is based on previous UTIs, effectiveness, and patient-specific factors such as allergies and cost. Antibiotics commonly used for recurrent UTIs can include sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, nitrofurantoin, cefaclor, or cephalexin.
In postmenopausal women with vaginal dryness that may be leading to recurrent UTIs, vaginal estrogen may be an effective treatment. Treatment options your doctor might recommend include: Estring, Vagifem , or vaginal estrogen creams .
Treatment Of Bladder Urinary Tract Infections
The specific intervention depends on the severity of the symptoms. In many instances, healthy patients who have a urinary tract infection but have no symptoms require no treatment at all. Such asymptomatic UTIs typically resolve within two to three days.
If urinary tract infection symptoms are presentsuch as a burning sensation during urination or an increased need to urinatetreatment usually consists of antibiotic medications, which are prescribed for three to 14 days. They include:
- Trimethoprim: Trimethoprim is the standard treatment for urinary tract infections in otherwise-healthy adults. It is one of the more potent UTI antibiotics, so most patients only require a three-day course. Trimethoprim is generally well-tolerated with few side effects, which generally include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea/constipation or stomach pain.
- Nitrofurantoin: Nitrofurantoin is the second most commonly prescribed antibiotic for bladder UTIs. It usually requires a longer course than trimethroprim , and is usually well tolerated but should not be taken by anyone with kidney disease. Side effects include nausea and vomiting.
- Cephalosporins: Cephalosporins are often used as a first-line of treatment in patients that have upper urinary tract infections involving the ureters or kidneys. It is usually taken for seven to 10 days. Side effects include nausea, vomiting, upset stomach and diarrhea.
Recommended Reading: Constant Bladder Infections After Intercourse
Medication For Urinary Tract Infection In Dogs
The aforementioned medications are used to treat a bacterial urinary infection in dogs. Non-bacterial infections are treated with other medications, such as fungicides and anti-parasitics. When there are blockages caused by stones or prostatitis, these problems should be treated at the same time as the infection. In addition, the veterinarian will recommend a diet that allows the normal pH of the urine to be restored, as it becomes alkaline during infection.
The prognosis depends on the complication of the infection, as well as the causative agents. Simple infections caused by bacteria usually have an excellent prognosis. In contrast, yeast infections are more difficult to treat. The most complicated urinary infections have a variable prognosis, depending on each case. Treatment is the same for male or female dogs, i.e. dependent on the udnerlying cause.
Also Check: Gynecologist Recommended Yeast Infection Treatment
Interpreting Home Test Results
These tests work similarly to a pregnancy test, using a test strip that a person wets with fresh urine.
After 12 minutes, the test strip will change color, indicating whether a UTI is present. A person must match the color of the test strip pads to the color blocks on the foil pouch in the test kit.
Most strips test for leukocytes and nitrites. Some also check pH levels.
Leukocytes are a type of white blood cell that helps the body fight off infection. Healthy urine contains chemicals called nitrates that can turn into nitrites if an infection is present. Therefore, the presence of leukocytes or nitrites in the urine is often a sign of a UTI.
Lastly, some home strips test pH levels. Healthy urine is slightly acidic, with a pH value in the range of . A pH level of 8.5 or 9 can indicate the presence of an infection and, therefore, a UTI.
If a home test is positive for any of these indicators, an individual likely has a UTI.
Don’t Miss: What Is A Tooth Infection Called
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection In Dogs
A urinary tract infection is a broad term for different types of infections which occur in the dogs urinary tract. The urinary tract is part of the dogs waste drainage system, getting rid of the waste biproducts of metabolism in the form of liquid urine. It is made up of the kidneys, ureters , the bladder and the urethra..
A UTI can occur randomly in any dog. However, those who suffer from a poor diet, do not have adequate hygiene care or are immunosuppressed are more susceptible to contracting one.
It should be noted that a urinary tract infection is not the same as cystitis. Although both terms are often used synonymously, cystitis specifically refers to inflammation of the dogs bladder. The two are often linked since such inflammation can be the result of a urinary tract infection, but it is not the only cause of cystitis in dogs. In this way, cystitis is a type of urinary tract infection, but it is not the only kind.
Generally, UTIs prohibit urination. If your dog is incontinent, it is usually due to another cause, although it can be related if they only produce a small amount.
You May Like: How To Treat Tooth Gum Infection At Home